Female Infidelity Gene AVPR1A Test
$149.00
Are you more likely to be unfaithful, because of your genes? Find out if have one of the “female infidelity” versions of the vasopressin receptor gene.
- Tests five genetic changes in the AVPR1A gene
- Women with one or more of these variants have an increased likelihood of extrapair mating or cheating
- 100% private and confidential online results
- Variants do not influence behavior in men
The “female infidelity” gene refers to five genetic variants of the AVPR1A gene. The AVPR1A gene encodes the arginine vasopressin receptor 1A, which binds vasopressin and transmits the signal into the cells.
Vasopressin is a hormone or “chemical messenger” that promotes water retention in the kidneys and increases blood pressure. Most of these effects take place when vasopressin is released into the blood stream. However, when vasopressin is released directly into the brain, it can influence social and sexual behavior (such as infidelity).
In women with the “female infidelity” versions of AVPR1A, the transmission of the vasopressin signal is disrupted. As such, each variant is associated with an increased likelihood of extrapair mating or cheating in women.
There is no evidence that these five variants influence sexual behavior in men. However, there is a different AVPR1A variation (known as the RS3 334 allele), which is associated with an increased likelihood of infidelity in men. The RS3 334 allele is detected in the Male Pair-Bonding Gene AVPR1A Test.
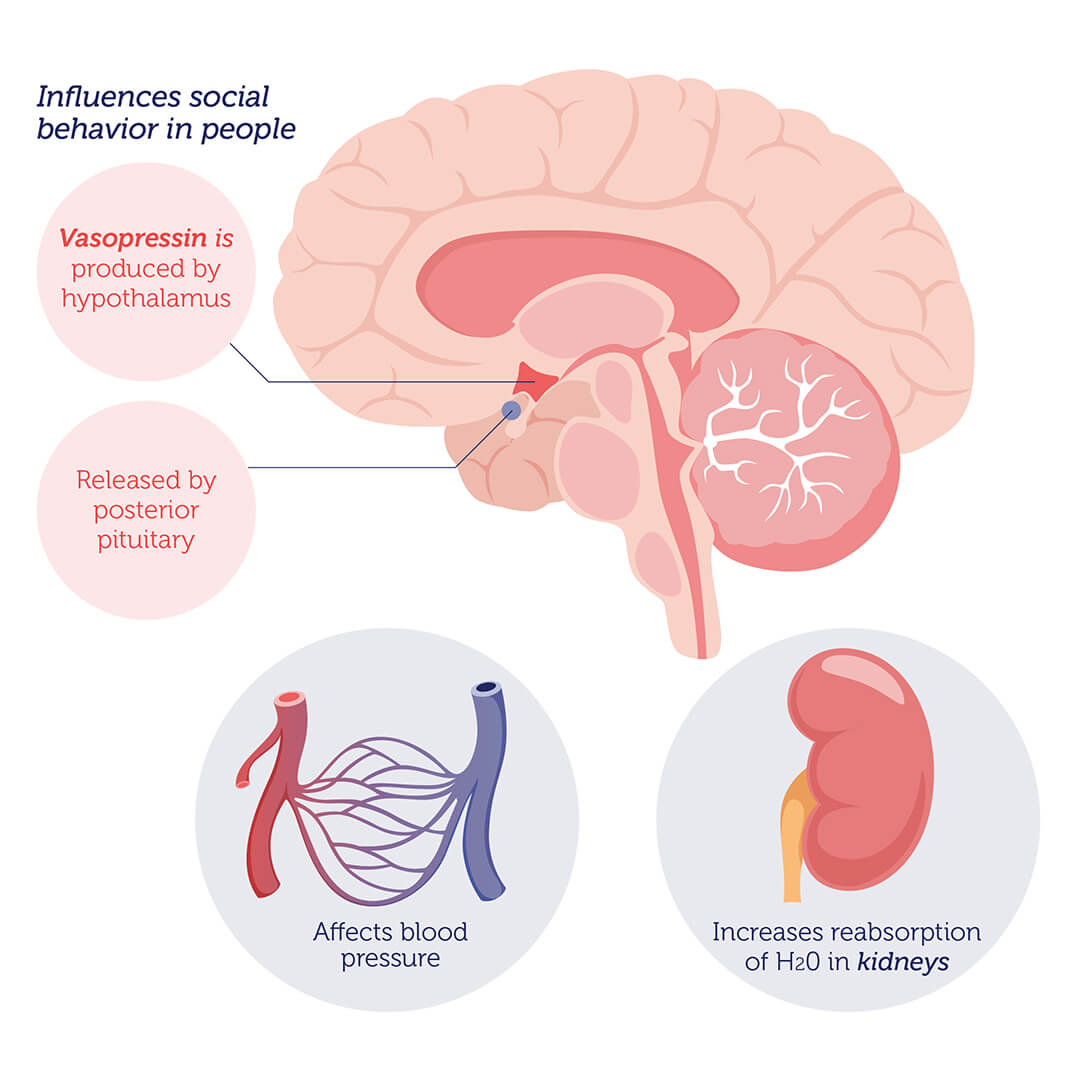

The AVPR1A gene is located on chromosome 12. We inherit two copies of the gene – one from each parent. A simple DNA test can be done to find out which forms of AVPR1A a person has inherited.
Genetic Variants Tested
The minor alleles (less common alleles) at these five markers in AVPR1A are linked to infidelity in women:
- rs10877970
- rs10877969
- rs3021529
- rs11174811
- rs1587097
Other Conditions Associated with the AVPR1A Gene
- Autism
- Altruistic behaviour
- Addictive behaviour
- Eating disorders
- Social behavior such as sibling interactions
How it works
Order your kit
Collect your sample
Receive your results
Related Products
$149.00
$149.00
$149.00
$149.00