Common STD Test
$129.00 Original price was: $129.00.$89.00Current price is: $89.00.
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis are common STDs that often go undetected. Our at-home Common STD Test Kit offers a convenient way to check for these infections from the privacy of your home. Get confidential results from our CLIA-certified lab and take charge of your sexual health.
Detects:
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- Trichomoniasis
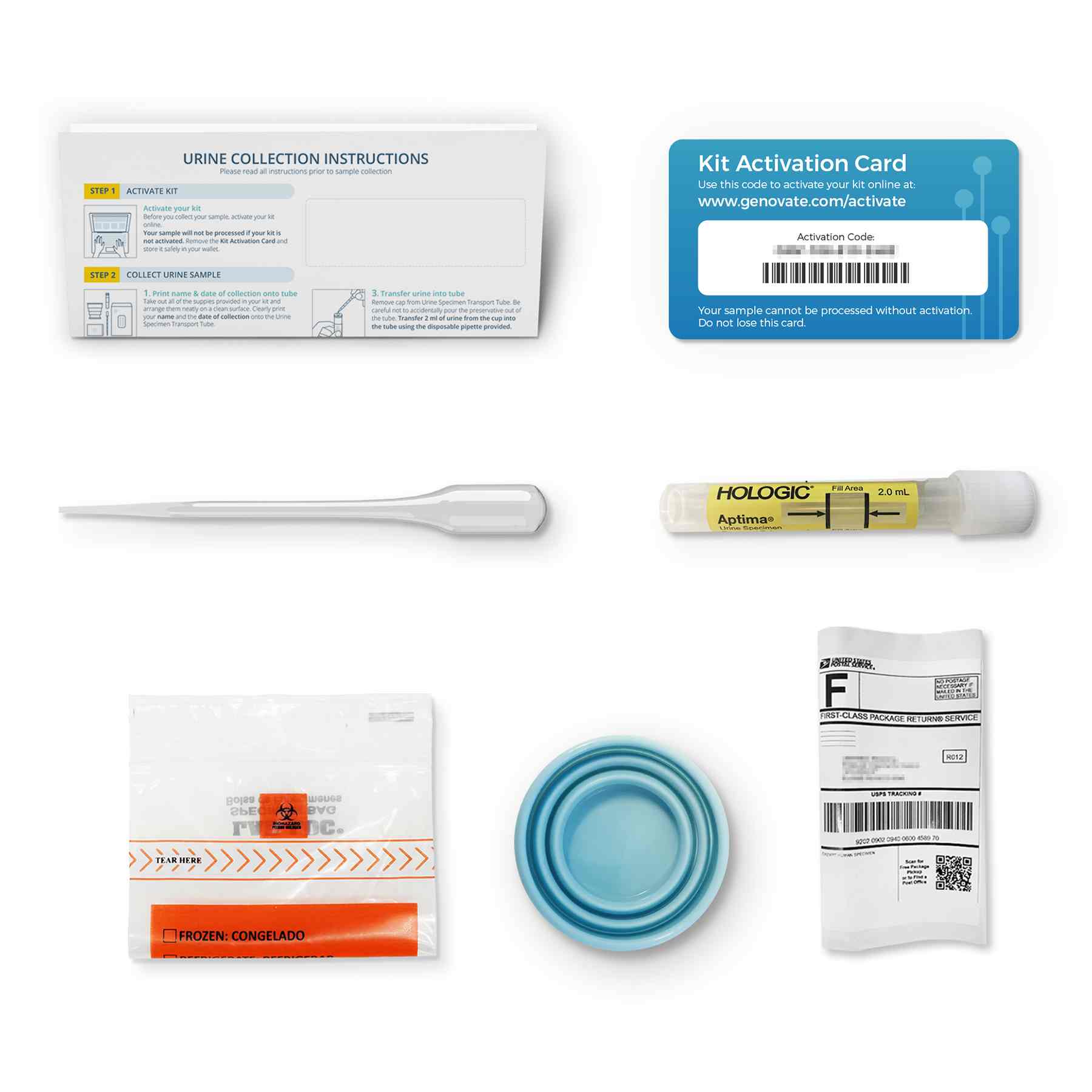
Collection Method: Urine
At-Home Screening for Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Trichomoniasis
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis are some of the most common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). These infections are easily spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex, and often go unnoticed because many people don’t have any symptoms. Without knowing it, you could be spreading an STD to others. If left untreated, these infections can lead to serious health problems in the future.
Fortunately, testing for these STDs is simple and easy with our at-home Common STD test kit. Say goodbye to uncomfortable clinic visits—our easy-to-use kit offers a discreet and convenient way to check for these infections right at home. Simply collect your samples, and then send them back to our CLIA-certified laboratory for analysis using the included return shipping supplies.
Early detection is key for effectively managing these conditions and preventing complications. That’s why getting tested regularly is so important—it’s the best way to protect yourself and your partners.
Order your Common STD Test Kit to take charge of your sexual health today!
Why Get Tested?
You should consider getting tested if:
- You are sexually active
- You have had unprotected sex
- You are entering a new relationship
- You are experiencing symptoms of an STD
- You have had a partner with an STD
Important Note: Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis have “window periods” where tests might miss an early infection. These periods are approximately two weeks for chlamydia and gonorrhea, and 3-6 weeks for trichomoniasis.
Symptoms of Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Trichomoniasis
Symptoms in Females
Endocervical bleeding
Increased urinary frequency
Rectal pain, swelling & bleeding
Painful urination
Vaginal discharge
Symptoms in Males
Testicular pain & swelling
Increased urinary frequency
Rectal pain, swelling & bleeding
Painful urination
Urethral discharge
What's included in this test?
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is an STD caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis. It’s the most commonly reported bacterial infection worldwide. Approximately 60% of new chlamydia infections occur in individuals aged between 15 and 24 years, with reported chlamydia rates in females being approximately two times the rate among males.
Chlamydia is diagnosed by nucleic acid amplification testing of vaginal swabs or urine specimens. Fortunately, chlamydia can be effectively treated with antibiotics. However, reinfections can occur through sexual contact with an infected partner, posing a risk of serious reproductive health complications.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is another common STD caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae. In women, this infection can impact the cervix, uterus, and fallopian tubes, while in men, it primarily affects the urethra. It can also infect the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes, and rectum.
Gonorrhea is typically diagnosed through nucleic acid amplification testing of vaginal swabs or urine samples. Gonorrhea is curable with dual antibiotic therapy. However, similar to chlamydia, repeat infections are common following sexual contact with an infected partner, increasing the risk of serious reproductive health complications.
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is caused by a protozoan parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. Infections occur in the lower genital tract, vulva, vagina, cervix, and urethra of women. The inside of the penis (urethra) is the most commonly infected body part of men. Most individuals infected with trichomoniasis remain asymptomatic, with only approximately 30% of infected individuals showing symptoms.
Trichomoniasis infections are associated with an increased risk of contracting other STDs, including a two to three-fold increased risk of HIV. Pregnant women with trichomoniasis have an increased risk of premature rupture of membranes, preterm delivery and giving birth to an infant with a low birth weight. Trichomoniasis is also associated with an increased risk of the transmission of HIV from an HIV-positive mother to her child.
Trichomoniasis is diagnosed by nucleic acid amplification testing of vaginal swabs or urine specimens. It is easily cured with antibiotics; however reinfections can occur after treatment through subsequent sexual contact with an infected partner.
How it works
Order your kit
Collect your sample
Receive your results
Our Laboratory Accreditations



FAQs
How does the Common STD Test work?
The process is simple. Collect a urine sample at home using the provided collection cup and transfer it into the sample vial. Next, mail the sample back to our CLIA-certified laboratory using the prepaid shipping envelope. At our CLIA-certified laboratory, we employ a highly sensitive technique known as nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) to detect bacterial DNA from chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis.
NAAT works by amplifying and replicating the DNA of these bacteria millions of times, enabling the detection of even the smallest amounts of bacterial DNA with extremely high sensitivity and accuracy. NAAT is known for its high sensitivity and quick processing time, making it the gold standard for detecting these STDs.
Why should I get tested?
STD testing is important because chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis are extremely common, especially among young adults aged 15-24. Many infected people don’t experience any symptoms, making testing the only way to know for sure if you’re infected. Early detection allows for effective treatment, helping to prevent long-term health issues. Getting tested protects both your health and the health of current or future sexual partners.
Is re-infection possible after treatment?
Yes, re-infection with chlamydia, gonorrhea, or trichomoniasis is possible after completing treatment if you are exposed to the STDs again. Successful antibiotic treatment cures the current infection but does not prevent future exposures or provide immunity.
What should I do if my test is positive?
If you receive a positive result, contact a healthcare professional immediately to discuss treatment options. It’s essential to follow your doctor’s recommendations carefully. Also, inform your sexual partners so they can get tested and treated if necessary.
How are chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis treated?
These infections are usually treated with a course of antibiotics. Your doctor will determine the specific type of antibiotic and how long you’ll need to take it. It’s important to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better, to ensure the infection is fully cleared. Both you and your sexual partner(s) should avoid sexual activity until treatment is finished to prevent reinfection.
Early diagnosis and consistent adherence to treatment are essential for effectively managing these infections. Please note that these are general guidelines, and the specific treatment for an individual will depend on their overall health, the stage of the disease, and other factors. Therefore, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice. Also, remember to complete the entire course of prescribed medication, even if symptoms improve before finishing the treatment.
How can I prevent these STDs?
To reduce your risk of contracting these STDs, consider the following preventive measures:
- Abstinence: The most reliable way to prevent STDs is to avoid sexual activity (vaginal, anal, and oral).
- Regular Testing: Get tested regularly, especially if you have multiple partners or engage in higher-risk behaviors. Early detection through tests can lead to timely treatment.
- Condoms: Condoms are effective in reducing the risk of STD transmission when used correctly and consistently during every sexual encounter.
- Limit Sexual Partners: Having fewer partners reduces your risk of exposure.
- Mutual Monogamy (only having one partner who only has you as a partner): Being in a mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested can significantly lower your risk.
- Avoid Sharing Needles: Never share needles, syringes, or other injecting equipment.
How common are chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis?
In the United States, chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis are three of the most common sexually transmitted infections. According to the most recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there were 1.6 million reported chlamydia cases in 2021, marking a 4.1% increase from 2020. Gonorrhea cases surpassed 700,000 in 2021, which is a 28% increase since 2017. For trichomoniasis, there were an estimated 2.6 million infections in 2018. The prevalence of trichomoniasis is 2.1% among women aged 14-59 and 0.5% among men, based on a national survey conducted from 2013-2016.
Are false-negative and false-positive results possible?
- False-negatives: A negative result doesn’t always guarantee you’re infection-free. These can happen if you test too soon after exposure (during the “window period”), if the sample isn’t collected correctly, or if you’re currently taking antibiotics.
- False-positives: These are less common but can occur, sometimes shortly after successful treatment when the test might still pick up traces of the bacteria.
Related Products
$149.00 Original price was: $149.00.$99.00Current price is: $99.00.
$99.00 Original price was: $99.00.$69.00Current price is: $69.00.